SQL 2016
To some of you SQL Server On Linux is old news from various announcements
Bob Ward and I worked with our SQL Server Tool developers (thanks David) to
20+ years ago when I joined Microsoft I was handed a diskette (maybe it
Back in July, I told you about a new installation experience for SQL Server.
These are distinct errors but I have found that many people blend them together.
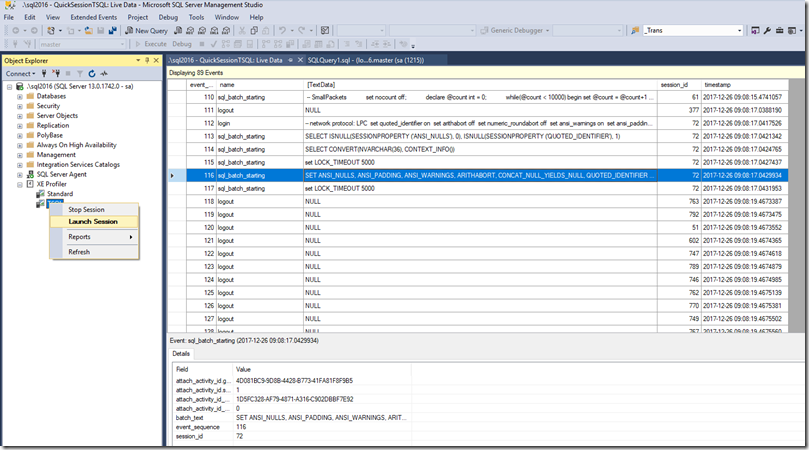
This blog takes you through the debugging journey, refreshing us on old concepts and
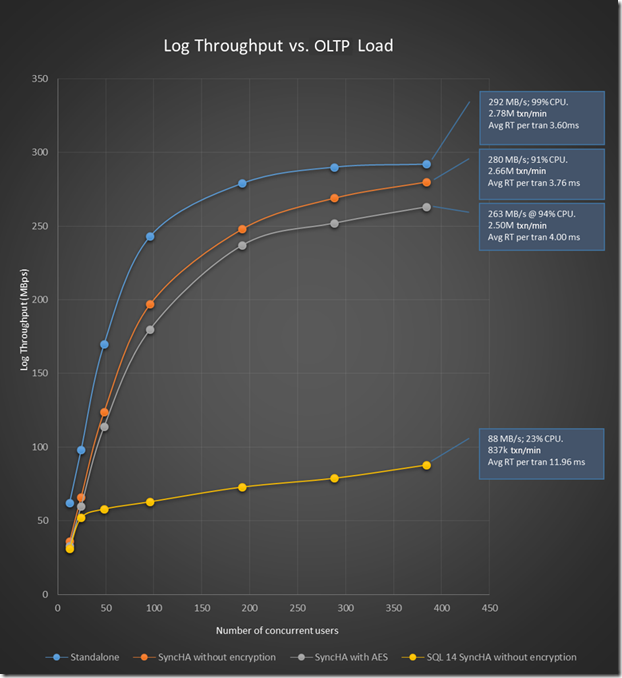
When we released Always On Availability Groups in SQL Server 2012 as a new
Database Instant File Initialization was added several SQL Server releases ago. The instant file
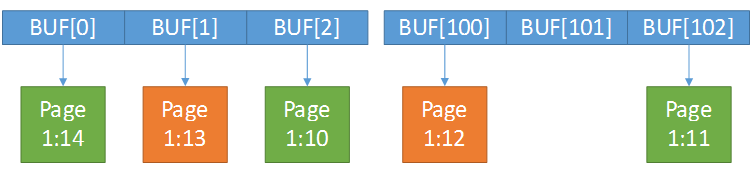
SQL Server uses WriteFileGather for the vast majority of data file write requests. The
When creating or growing the database log file (LDF) a byte pattern is stamped.